Arrangement of Resistors in Circuits
Arrangement of Resistors in Circuits: Overview
This topic covers concepts such as, Resistors in Parallel Combination, Equivalent Resistance in Series Combination, Distribution of Current in Parallel Resistors and Distribution of Potential in Series Resistors etc.
Important Questions on Arrangement of Resistors in Circuits
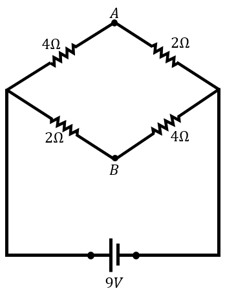
(i) Calculate the equivalent resistance of the given electrical network between points and .
(ii) Also calculate the current through , if a source is connected between and , and the value of is assumed as .
You are given resistors, each of resistance . These are first connected to get the minimum possible resistance. In the second case, these are again connected differently to get maximum possible resistance. The ratio between the minimum and maximum values of resistance so obtained is
You are given ‘n’ resistors, each of resistance ‘r’. These are first connected to get minimum possible resistance. In the second case, these are again connected differently to get maximum possible resistance. The ratio between the minimum and maximum values of resistance so obtained is
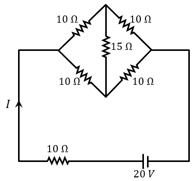
In the circuit, shown in the figure, the ammeter reading is
A wire is broken in four equal parts. A packet is formed by keeping the four wires together. The resistance of the packet in comparison to the resistance of the wire will be
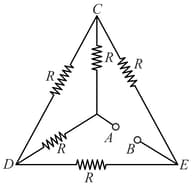
Find the magnitude of potential difference (in ) between A and B in the given circuit.
resistors each of resistance when connected together give minimum equivalent resistance and maximum equivalent resistance among various possible combinations. So is equal to
The equivalent resistance of the network shown in figure betweenand is
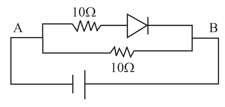
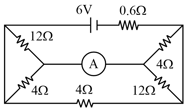
The current in the circuit is
In the given dc circuit, a voltmeter whose resistance is is used to measure the voltage drop across the resistor. Determine the difference in the voltmeter reading that is observed when compared to the true voltage across resistor when the voltmeter is not connected.
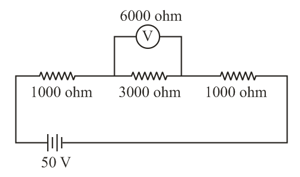
Consider the following electric circuit
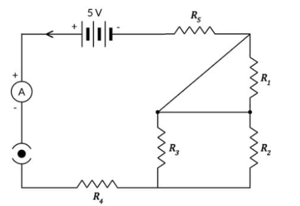
1) Which two resistors are connected in series?
2) Which two resistors are connected in parallel?
3) If every resistor is , what current will flow in the circuit?
The resistance of , , and are connected as shown in the circuit. Find the resultant resistance in the circuit.
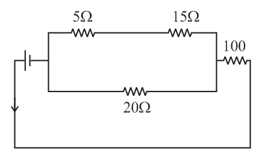
For the following circuit, the potential difference between x and y is
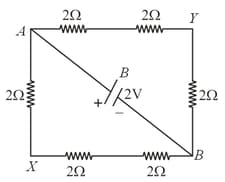
If we connect two resistance in series then their equivalent resistance is 25 ohm and if we connect them in parallel then it is 4 ohm. What is the value of each resistance?
An infinite ladder network of resistances is constructed with and resistances. The battery between and has negligible internal resistance. The equivalent resistance between and is
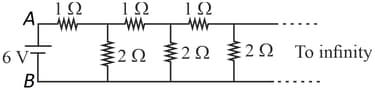
Consider the figure shown below. The resistance of the arrangement between the terminals and is:
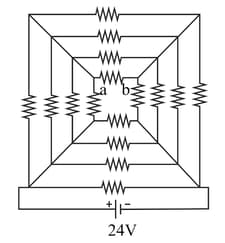
The figure shows a circuit in which sixteen resistors each of resistance are connected to a battery of emf . The current in branch is
'' identical resistors are taken. '' resistors are connected in series and the remaining are connected in parallel. The series connected group is kept in the left gap of a meter bridge and the parallel connected group in the right gap. The distance of the balance point in cm from the left end of the wire is
Find the equivalent resistance between the points A and B for the following figure.
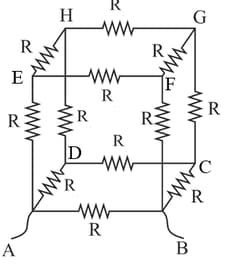
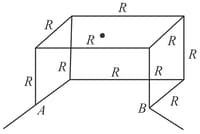
Twelve wires each of resistance ohm are connected in the form of a skeleton cube. Find the equivalent resistance of the cube when a cell is connected across any one of the wires forming the cube.